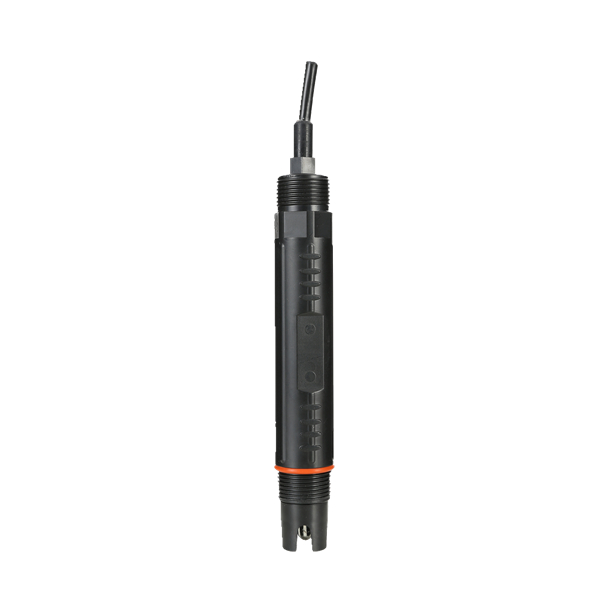
Basic Principle of pH Electrode
In PH measurement, the used pH electrode is also known as the primary battery. The primary battery is a system, whose role is to transfer chemical energy into electrical energy. The voltage of the battery is called the electromotive force (EMF). This electromotive force (EMF) is composed of two half-batteries. One half-battery is called the measuring electrode, and its potential is related to the specific ion activity; the other half-battery is the reference battery, often called the reference electrode, which is generally interlinked with the measurement solution, and connected to the measuring instrument.
Features
1. It adopts the world-class solid dielectric and a large area of PTFE liquid for junction, difficult to block and easy to maintain.
2. Long-distance reference diffusion channel greatly extends the service life of electrodes in the harsh environment.
3. There is no need for additional dielectric and there is a little amount of maintenance.
4. High accuracy, fast response and good repeatability.
Technical Indexes
| Model No.: PH8011 pH Sensor | |
| Measuring range: 7-9PH | Temperature range: 0-60℃ |
| Compressive strength: 0.6MPa | Material: PPS/PC |
| Installation Size: Upper and Lower 3/4NPT Pipe Thread | |
| Connection: Low-noise cable goes out directly. | |
| The antimony is relatively sturdy and corrosion-resistant, which meets the requirements for solid electrodes, | |
| corrosion resistance and the measurement of the water body containing hydrofluoric acid, such as the | |
| wastewater treatment in semiconductors and iron and steel industries. The antimony-sensitive film is used for | |
| the industries corrosive to the glass. But there are also limitations. If the measured ingredients are replaced by | |
| antimony or react with antimony to produce complex ions, they should not be used. | |
| Note: Keep the antimony electrode surface cleaning; if necessary, use the fine | |
| Sandpaper to polish the surface of antimony. | |
Why monitor the pH of water?
pH measurement is a key step in many water testing and purification processes:
● A change in the pH level of water can alter the behavior of chemicals in the water.
● pH affects product quality and consumer safety. Changes in pH can alter flavor, color, shelf-life, product stability and acidity.
● Inadequate pH of tap water can cause corrosion in the distribution system and can allow harmful heavy metals to leach out.
● Managing industrial water pH environments helps prevent corrosion and damage to equipment.
● In natural environments, pH can affect plants and animals.




















