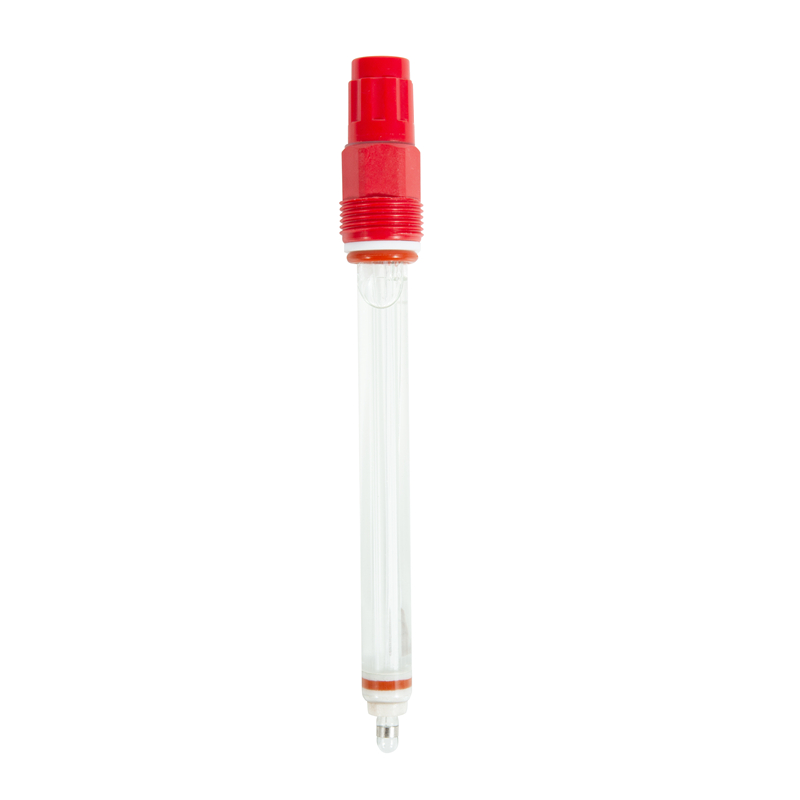
Introduction
The high temperature ORP electrode is independently developed by BOQU and has independent intellectual property rights.BOQU Instrument also built first high temperature labotary in China.Hygienic and high temperature ORP electrodes for aseptic applications are readily available for applications where in-situ cleaning (CIP) and in-situ sterilization (SIP) are often performed. These ORP electrodes are resistant to the high temperatures and fast media transitions of these processes and are still in precision measurements without maintenance interruptions.These hygienic ORP electrodes help you meet regulatory compliance requirements for pharmaceutical, biotech and food/beverage production.Options for liquid, gel and polymer reference solution which ensure your requirements for accuracy and working life. and the high pressure design is good for installation in tank and reactors.


Technical Indexes
| Parameter measure | ORP |
| Measuring range | ±1999mV |
| Temperature range | 0-130℃ |
| Accuracy | ±=1mV |
| Compressive strength | 0.6MPa |
| Temperature compensation | No |
| Socket | K8S |
| Cable | AK9 |
| Dimensions | 12x120, 150, 225, 275 and 325mm |
Features
1. It adopts heat-resisting gel dielectric and solid dielectric double liquid junction structure; in the circumstances when the electrode is not connected to
the back pressure, the withstand pressure is 0~6Bar. It can be directly used for l30℃ sterilization.
2. There is no need for additional dielectric and there is a little amount of maintenance.
3. It adopts S8 or K8S and PGl3.5 thread socket, which can be replaced by any overseas electrode.
Field of application
Bio-engineering: Amino acids, blood products, gene, insulin and interferon.
Pharmaceutical industry: Antibiotics, vitamins and citric acid
Beer: Brewing, mashing, boiling, fermentation, bottling, cold wort and deoxy water
Food and beverages: On-line measurement for MSG, soy sauce, dairy products, juice, yeast, sugar, drinking water and other bio-chemical process.
What is ORP?
Oxidation Reduction Potential (ORP or Redox Potential) measures an aqueous system’s capacity to either release or accept electrons from chemical reactions.
When a system tends to accept electrons, it is an oxidizing system. When it tends to release electrons, it is a reducing system. A system’s reduction potential may
change upon introduction of a new species or when the concentration of an existing species changes.
ORP values are used much like pH values to determine water quality. Just as pH values indicate a system’s relative state for receiving or donating hydrogen ions,
ORP values characterize a system’s relative state for gaining or losing electrons. ORP values are affected by all oxidizing and reducing agents, not just acids
and bases that influence pH measurement.




















